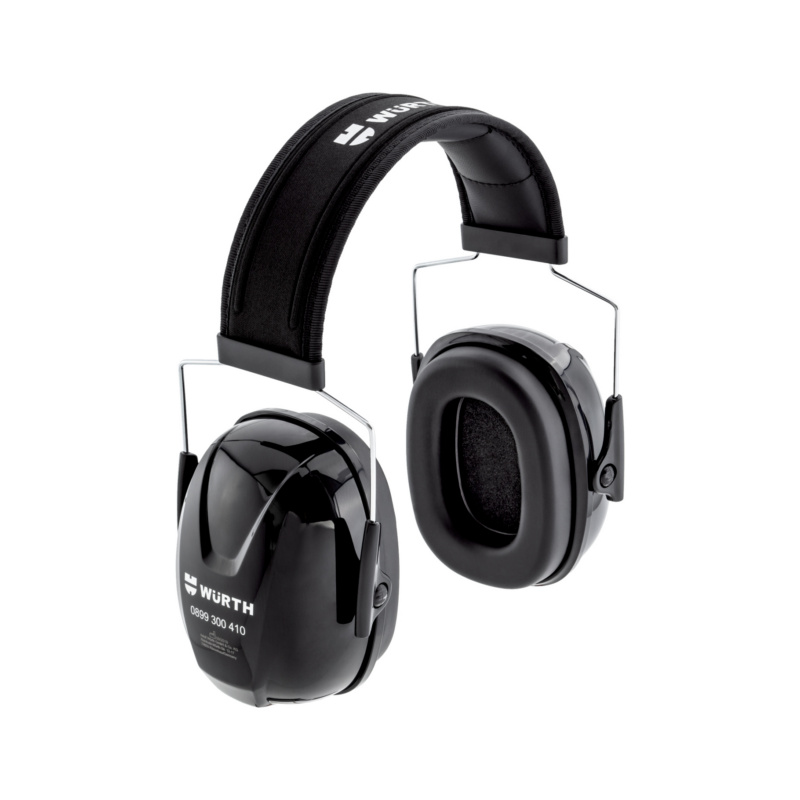
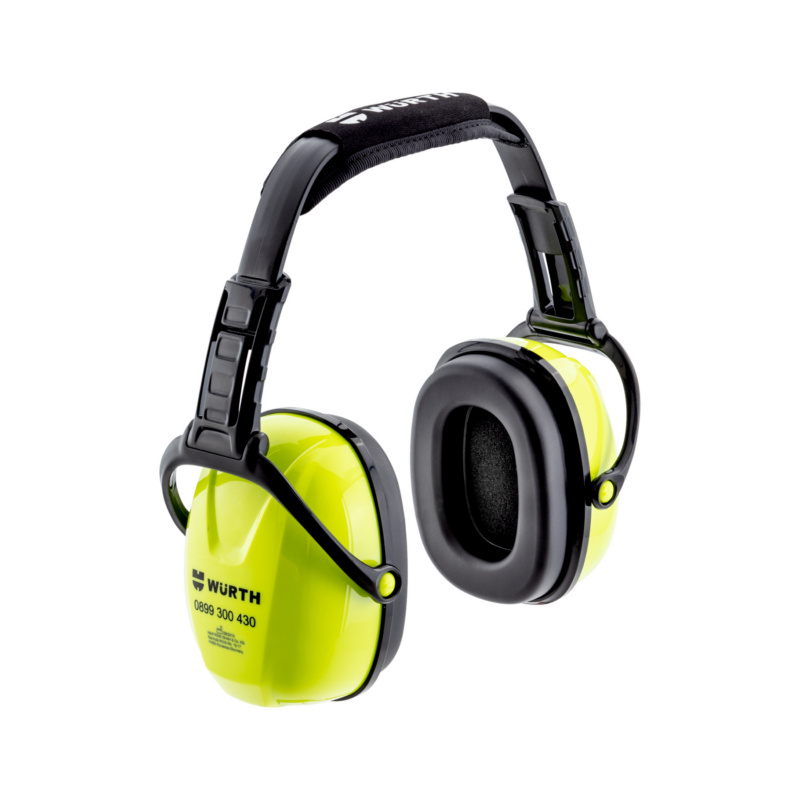
Hearing Protection: Safe and Sound
What is noise?
Noise is considered to be any unwanted loud sound, the perception of which is subjective. Sound is caused by the perception of vibrations that travel through the air as sound waves. The sound pressure level can be measured and is expressed in decibels (dB). Above 80 dB, the employer must provide suitable hearing protection devices. Above 85 dB, the wearing of a hearing protection device is mandatory and noisy areas must be indicated as such.

What are insulation values?
Two factors are decisive in determining the right hearing protection device: the noise level in the working environment and the insulation level of the hearing protection device. In terms of insulation values, a distinction is made between HML values and the SNR value. The HML values indicate the insulation performance at high (H), medium (M) or low (L) frequency respectively. The SNR (single number rating) value indicates the average insulation performance. Calculation using the SNR value is decisive in selecting the correct hearing protection device.
The noise level minus the insulation value results in the residual sound value. This should be in a range below 80 dB to prevent damage to hearing. Normal performance can be reduced due to incorrect wearing. This is because the insulating performance of the hearing protection device can be reduced by having a beard or longer hair, wearing goggles, by contamination or where ear plugs are incorrectly inserted.
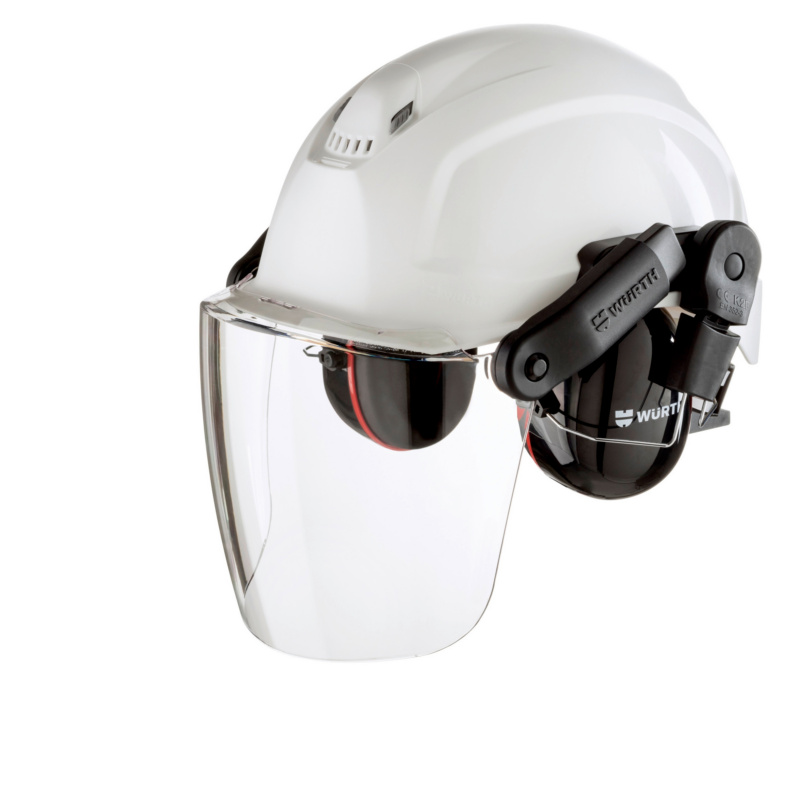

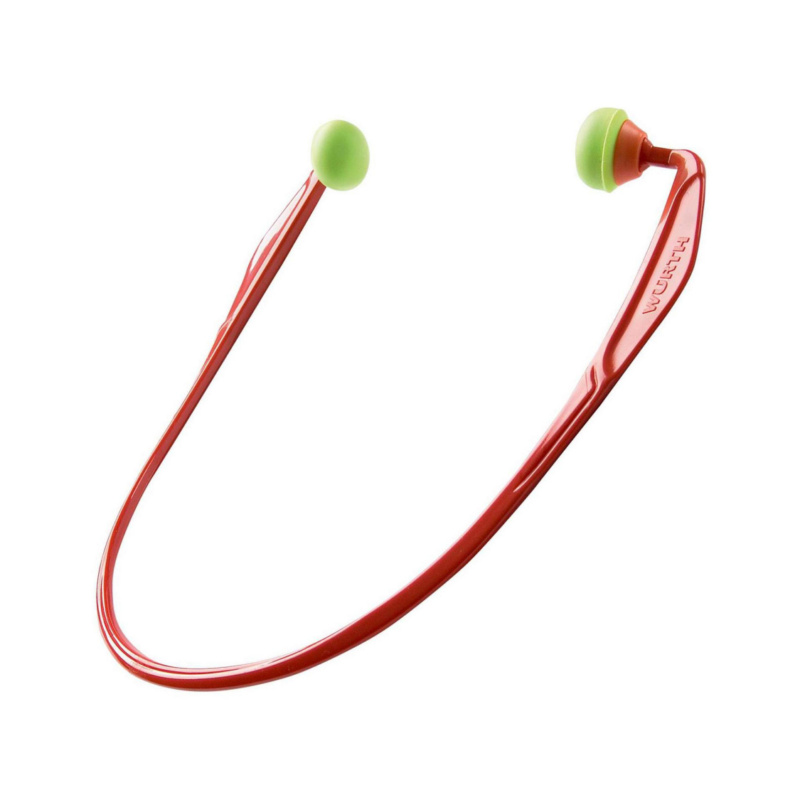
Are you looking for the right hearing protection device for the construction site?
Use our SH 2000-S hard hat in combination with ear defenders for complete protection!
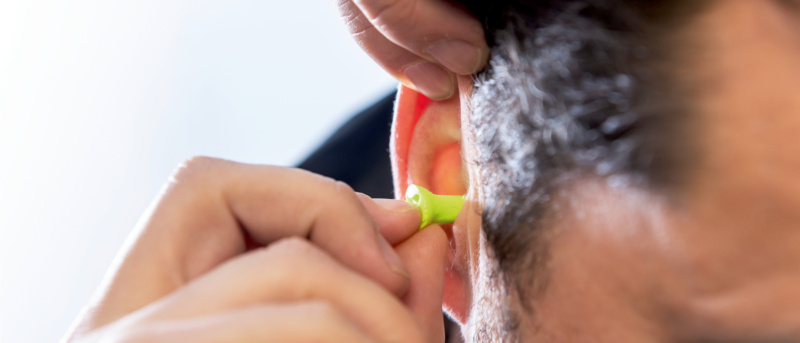
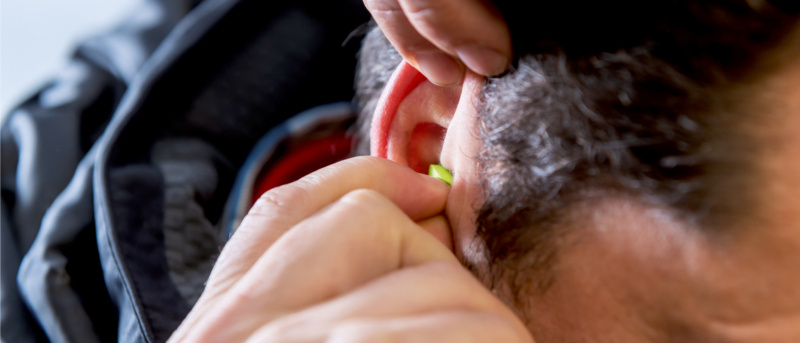
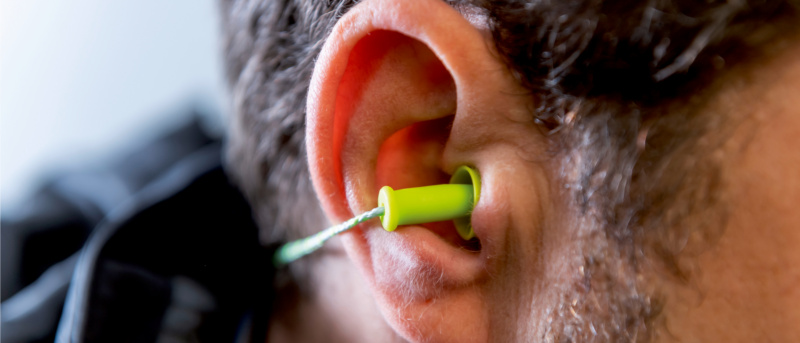
Hearing protection device worn incorrectly offers only partial protection or none at all. Therefore, observe the following procedure when inserting ear plugs.
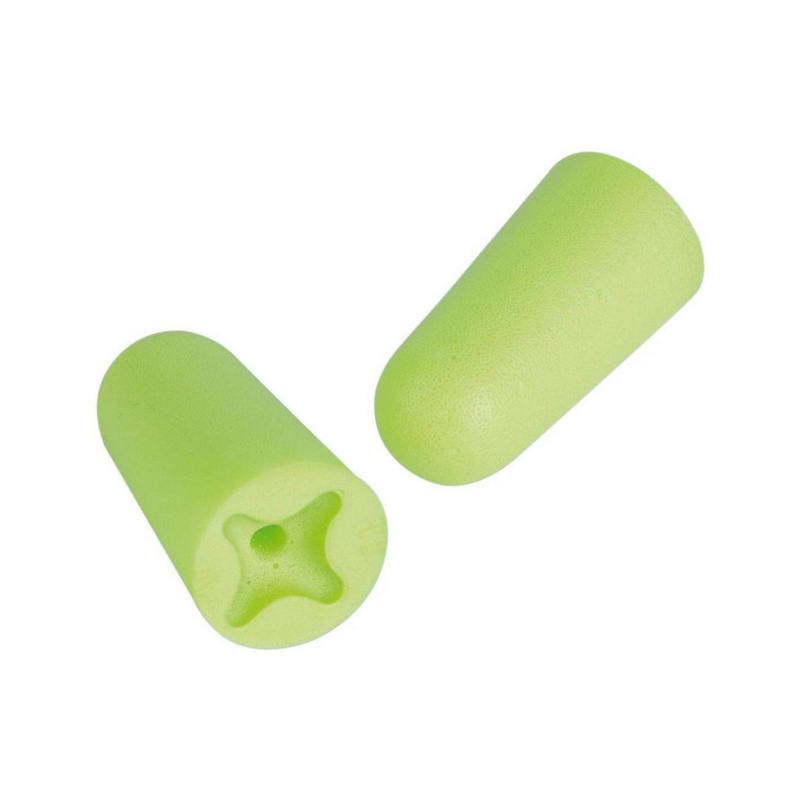
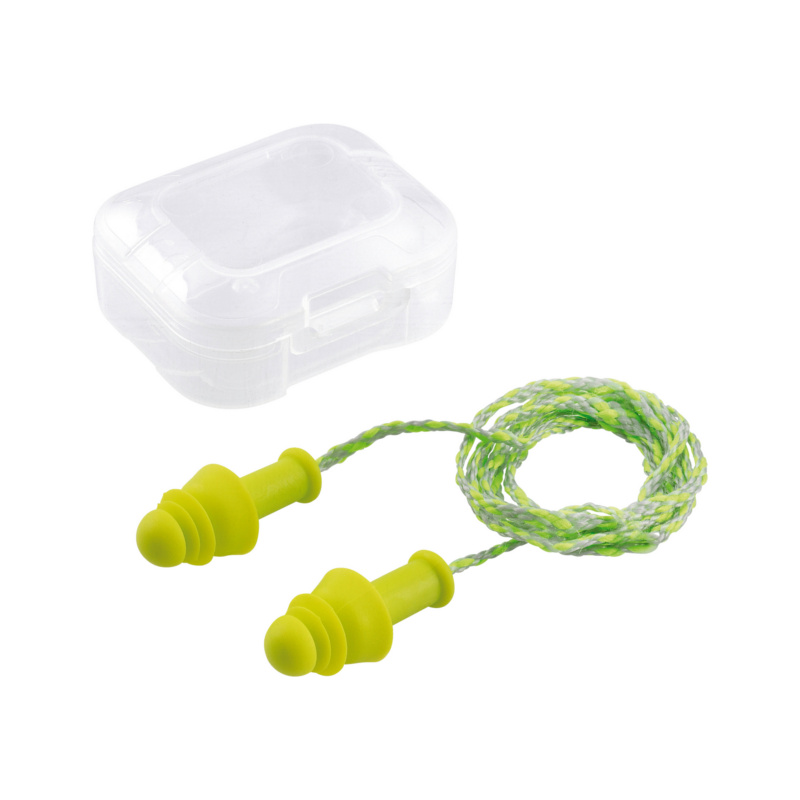
Disposable ear plugs
Note: Please discard the ear plug after each use.
Reusable or finned ear plugs
Note: Finned ear plugs can be worn multiple times. Clean the plugs with water and mild soap and store them in the convenient box.
The Adolf Würth GmbH & Co. KG collects and processes the personal data provided in the form in order to process the requested request for you. Please note the mandatory fields in the forms. The legal basis for this processing, the absolutely necessary data, is Art. 6 para. 1 lit. b GDPR, implementation of a pre-contractual measure. The processing of data voluntarily provided by you is carried out on the basis of Art. 6 para. 1 lit. f GDPR. Thereafter, processing is permissible which is necessary to safeguard our legitimate interests. Our legitimate interest is to have contact with you, our customers, to improve our consulting quality and to be able to contact you more easily in case of possible queries. The data collected will only be stored by us for as long as is necessary to process your enquiry and to contact you. They are then deleted.
Supplementary data protection information, in particular regarding your rights to information, correction, deletion, restriction of processing, objection and complaint, can be found in our data protection declaration.